The tomato is one of the most widely grown and consumed crops in the world. Found in kitchens, farms, and gardens across the globe, tomatoes are valued for their taste, nutrition, and versatility. From fresh salads to sauces and soups, tomatoes play a major role in daily meals.
Beyond cooking, tomatoes are also important in agriculture, medicine, and scientific research. Understanding the tomato scientific name, its plant structure, types, health benefits, and cultivation needs helps gardeners, students, and food lovers appreciate this remarkable plant even more.
What Is the Scientific Name of Tomato?
The scientific name of tomato is Solanum lycopersicum.
This name is recognized internationally and is used by scientists, farmers, and researchers to identify the tomato plant accurately.
Scientific names are written in Latin to ensure the same name is used worldwide. While tomatoes may have different common names in different countries, their scientific name remains the same everywhere.
Tomatoes belong to the nightshade family, which also includes potatoes, eggplants, and peppers. Using the scientific name helps avoid confusion and ensures accurate communication in agriculture and biology.
Botanical Classification of Tomato
The tomato plant is classified using a hierarchical system that groups plants based on shared characteristics.
| Classification Level | Name |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Clade | Angiosperms |
| Clade | Eudicots |
| Order | Solanales |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Genus | Solanum |
| Species | Solanum lycopersicum |
This classification places tomatoes among flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruit.
Meaning and Pronunciation of Tomato
Scientific names often carry historical or descriptive meanings. The tomato scientific name reflects ancient beliefs and plant characteristics.
Meaning of Tomato Scientific Name
- Solanum: A Latin word referring to the nightshade family
- Lyco: Greek word meaning “wolf”
- Persicum: Latin word meaning “peach”
The term “wolf peach” came from old European beliefs that tomatoes were poisonous. Today, science has proven tomatoes to be safe and extremely healthy.
Pronunciation of Tomato Scientific Name
- Solanum – suh-LAY-num
- Lycopersicum – ly-koh-PER-si-kum
- Full name – suh-LAY-num ly-koh-PER-si-kum
Correct pronunciation is helpful in academic and scientific discussions.
Origin and History of the Tomato Plant
Tomatoes originated in western South America, particularly in regions of present-day Mexico and Peru. Wild tomato varieties were first domesticated by indigenous civilizations thousands of years ago.
The Aztecs cultivated tomatoes and used them in their cooking long before Europeans arrived. Spanish explorers introduced tomatoes to Europe in the 16th century. At first, Europeans believed tomatoes were toxic and grew them only as ornamental plants.
Over time, tomatoes became popular in Mediterranean cuisine, especially in Italy. Eventually, tomatoes spread worldwide and became one of the most important food crops globally.
Today, billions of tomatoes are grown annually in different climates and regions.
Structure, Size, and Growth of a Tomato Plant
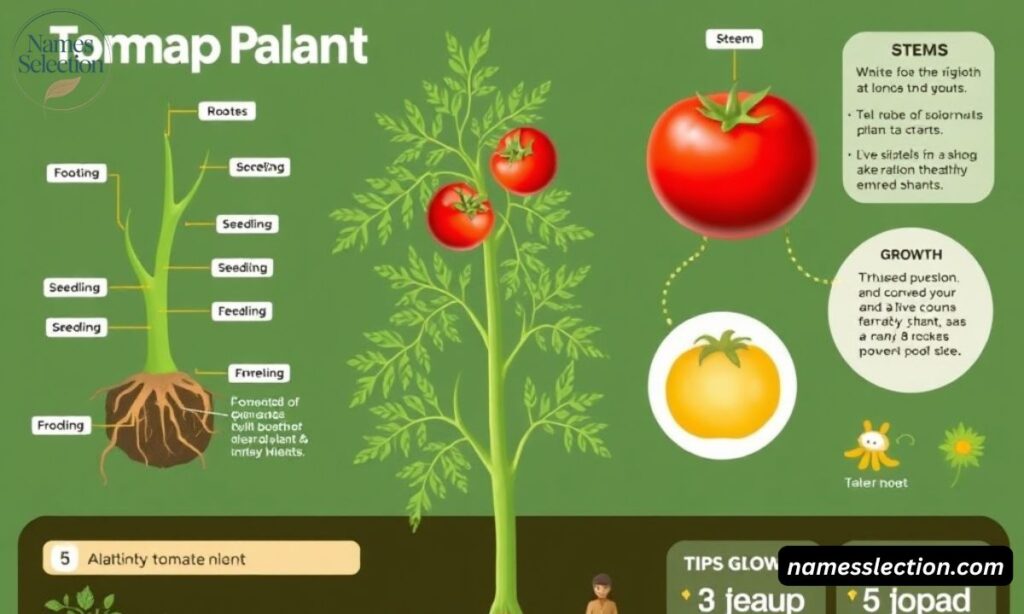
The tomato plant is a soft-stemmed, herbaceous plant that grows rapidly in warm conditions. It can be grown as an annual plant in most climates.
Tomato plants vary in size depending on the variety. Some remain compact, while others grow tall and require support.
Key Features
- Height: 3 to 10 feet depending on variety
- Stem: Green, soft, and hairy
- Leaves: Large, compound, and deeply lobed
- Roots: Fibrous root system spreading wide
- Flowers: Small, yellow, star-shaped
- Fruit: Fleshy berries containing many seeds
Tomato plants are dicots, meaning they produce two seed leaves during germination.
Is a Tomato a Fruit or a Vegetable?
This is one of the most common questions about tomatoes.
Scientifically
From a botanical perspective, tomatoes are fruits. They develop from the flower’s ovary and contain seeds. Botanically, tomatoes are classified as berries.
In Cooking
In culinary use, tomatoes are considered vegetables because of their savory taste. They are used in salads, sauces, soups, and main dishes rather than desserts.
Fun Fact
In 1893, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that tomatoes should be classified as vegetables for taxation purposes. This legal decision still influences how people think about tomatoes today.
Tomato Types and Varieties
There are hundreds of tomato varieties grown worldwide. Each type has unique characteristics, flavors, and uses.
Common tomato types include:
- Cherry tomatoes – Small, sweet, and round
- Grape tomatoes – Oval-shaped with firm flesh
- Roma tomatoes – Meaty and ideal for sauces
- Beefsteak tomatoes – Large and juicy
- Heirloom tomatoes – Traditional varieties with rich flavor
Different varieties are chosen based on climate, disease resistance, and intended use.
Tomato Size, Shape, and Nutrition

Tomato Size and Shape
Tomatoes range from tiny cherry-sized fruits to very large beefsteak varieties.
| Variety | Average Size | Weight |
| Cherry | 1–2 cm | 10–20 g |
| Roma | 5–7 cm | 50–80 g |
| Beefsteak | 10–12 cm | 200–500 g |
Tomatoes come in many colors including red, yellow, orange, green, purple, and striped.
Nutritional Benefits of Tomatoes
Tomatoes are low in calories but rich in nutrients.
Per 100g Raw
- Calories: 18
- Water: 95%
- Carbohydrates: 3.9 g
- Fiber: 1.2 g
- Vitamin C: 21% of daily needs
- Potassium: Supports heart health
- Lycopene: Powerful antioxidant
Key Health Benefits
- Improves heart health
- Strengthens immunity
- Supports healthy skin
- Protects eyesight
- Helps digestion
- Aids weight management
- Reduces inflammation
Cooking tomatoes increases lycopene absorption, making sauces especially healthy.
Tomato Plant Leaves and Flowers
Tomato Leaf
Tomato leaves are compound with jagged edges and a strong smell. They help with photosynthesis but should not be eaten, as they contain toxic compounds.
Tomato Flower
Tomato flowers are small, yellow, and star-shaped. They are self-pollinating and usually appear 30–45 days after planting.
Tomato Plant Life Cycle and Development Stages
The tomato plant follows a clear growth cycle.
| Stage | Time | Description |
| Germination | 5–10 days | Seed sprouts |
| Seedling | 2–3 weeks | Leaves develop |
| Vegetative | 3–5 weeks | Rapid growth |
| Flowering | 6 weeks | Flowers appear |
| Fruiting | 7–10 weeks | Fruit forms |
| Ripening | 10–12 weeks | Tomatoes mature |
Climate, Soil, and Cultivation Requirements for Tomato
Tomatoes grow best in warm, sunny environments.
- Temperature: 65–85°F
- Sunlight: 6–8 hours daily
- Soil pH: 6.0–6.8
- Soil Type: Well-drained, fertile soil
- Watering: Regular but not excessive
- Support: Stakes or cages
Proper care leads to healthy plants and high yields.
Common Diseases and Pests of Tomato Plant
Tomato plants are vulnerable to several diseases and pests.
- Early blight
- Late blight
- Tomato hornworms
- Aphids
- Fusarium wilt
- Blossom end rot
Preventive care and good farming practices reduce risks.
Common Uses of Tomatoes
Culinary Uses
- Salads and sandwiches
- Sauces and soups
- Ketchup and juice
- Curries and stews
- Canning and drying
Non-Food Uses
- Skincare treatments
- Lycopene supplements
- Composting
- Natural dyes
Conventional and Medicinal Uses of Tomato
Tomatoes have long been used in traditional medicine.
- Supports digestion
- Helps regulate blood pressure
- Reduces inflammation
- Improves skin healing
- Supports heart health
Modern science supports many of these benefits.
Quick Facts About the Tomato
| Feature | Detail |
| Scientific Name | Solanum lycopersicum |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Origin | South America |
| Fruit Type | Berry |
| Calories | 18 per 100g |
| Growth Time | 75–100 days |
Last Words
The tomato scientific name Solanum lycopersicum represents one of the most valuable plants in human history. From ancient civilizations to modern kitchens, tomatoes have shaped diets, agriculture, and culture worldwide.
Rich in nutrients, easy to grow, and incredibly versatile, tomatoes remain a staple food across the globe. Understanding their scientific background and benefits helps us appreciate this humble yet powerful plant even more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scientific name for tomatoes?
Solanum lycopersicum.
Is tomato a fruit or vegetable?
Botanically a fruit, culinarily a vegetable.
Are tomato leaves edible?
No, they are toxic.
What nutrients are in tomatoes?
Vitamin C, potassium, fiber, and lycopene.
How long does a tomato plant take to grow?
Around 75–100 days.

Charlotte, founder of Namesslection.com, shares her passion for creativity through Funny Names, Cute Names, and Other Names. She helps people find unique, fun, and meaningful names with ease.








